The poisson solver example.
This example depends on simple-solver.
Introduction
This example solves a 1D Poisson equation:
![$ u : [0, 1] \rightarrow R\\ u'' = f\\ u(0) = u0\\ u(1) = u1 $](form_15.png)
using a finite difference method on an equidistant grid with K discretization points (K can be controlled with a command line parameter). The discretization is done via the second order Taylor polynomial:
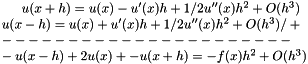
For an equidistant grid with K "inner" discretization points 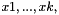 and step size
and step size 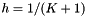 , the formula produces a system of linear equations
, the formula produces a system of linear equations
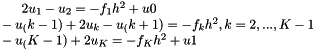
which is then solved using Ginkgo's implementation of the CG method preconditioned with block-Jacobi. It is also possible to specify on which executor Ginkgo will solve the system via the command line. The function 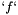 is set to
is set to 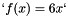 (making the solution
(making the solution 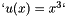 ), but that can be changed in the
), but that can be changed in the main function.
The intention of the example is to show how Ginkgo can be used to build an application solving a real-world problem, which includes a solution of a large, sparse linear system as a component.
About the example
The commented program
#include <ginkgo/ginkgo.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
Creates a stencil matrix in CSR format for the given number of discretization points.
{
const auto discretization_points = matrix->
get_size()[0];
int pos = 0;
const double coefs[] = {-1, 2, -1};
row_ptrs[0] = pos;
for (int i = 0; i < discretization_points; ++i) {
for (auto ofs : {-1, 0, 1}) {
if (0 <= i + ofs && i + ofs < discretization_points) {
values[pos] = coefs[ofs + 1];
col_idxs[pos] = i + ofs;
++pos;
}
}
row_ptrs[i + 1] = pos;
}
}
Generates the RHS vector given f and the boundary conditions.
template <typename Closure>
{
const auto discretization_points = rhs->
get_size()[0];
const auto h = 1.0 / (discretization_points + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < discretization_points; ++i) {
const auto xi = (i + 1) * h;
values[i] = -f(xi) * h * h;
}
values[0] += u0;
values[discretization_points - 1] += u1;
}
Prints the solution u.
{
std::cout << u0 << '\n';
for (
int i = 0; i < u->
get_size()[0]; ++i) {
}
std::cout << u1 << std::endl;
}
Computes the 1-norm of the error given the computed u and the correct solution function correct_u.
template <typename Closure>
Closure correct_u)
{
const auto h = 1.0 / (discretization_points + 1);
auto error = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < discretization_points; ++i) {
using std::abs;
const auto xi = (i + 1) * h;
error +=
}
return error;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Some shortcuts
using vec = gko::matrix::Dense<double>;
if (argc < 2) {
std::cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " DISCRETIZATION_POINTS [executor]"
<< std::endl;
std::exit(-1);
}
Get number of discretization points
const unsigned int discretization_points =
argc >= 2 ? std::atoi(argv[1]) : 100;
const auto executor_string = argc >= 3 ? argv[2] : "reference";
Figure out where to run the code
std::map<std::string, std::shared_ptr<gko::Executor>> exec_map{
{"omp", omp},
{"reference", gko::ReferenceExecutor::create()}};
executor where Ginkgo will perform the computation
const auto exec = exec_map.at(executor_string);
executor used by the application
const auto app_exec = exec_map["omp"];
problem:
auto correct_u = [](double x) { return x * x * x; };
auto f = [](double x) { return 6 * x; };
auto u0 = correct_u(0);
auto u1 = correct_u(1);
initialize matrix and vectors
auto matrix = mtx::create(app_exec,
gko::dim<2>(discretization_points),
3 * discretization_points - 2);
generate_stencil_matrix(
lend(matrix));
auto rhs = vec::create(app_exec,
gko::dim<2>(discretization_points, 1));
generate_rhs(f, u0, u1,
lend(rhs));
auto u = vec::create(app_exec,
gko::dim<2>(discretization_points, 1));
for (
int i = 0; i < u->
get_size()[0]; ++i) {
}
Generate solver and solve the system
cg::build()
.with_criteria(gko::stop::Iteration::build()
.with_max_iters(discretization_points)
.on(exec),
.with_reduction_factor(1e-6)
.on(exec))
.with_preconditioner(bj::build().on(exec))
.on(exec)
->generate(
clone(exec, matrix))
print_solution(u0, u1,
lend(u));
std::cout << "The average relative error is "
<< calculate_error(discretization_points,
lend(u), correct_u) /
discretization_points
<< std::endl;
}
Results
This is the expected output:
0
0.00010798
0.000863838
0.00291545
0.0069107
0.0134975
0.0233236
0.037037
0.0552856
0.0787172
0.10798
0.143721
0.186589
0.237231
0.296296
0.364431
0.442285
0.530504
0.629738
0.740633
0.863838
1
The average relative error is 1.87318e-15
Comments about programming and debugging
The plain program
#include <ginkgo/ginkgo.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
{
const auto discretization_points = matrix->
get_size()[0];
int pos = 0;
const double coefs[] = {-1, 2, -1};
row_ptrs[0] = pos;
for (int i = 0; i < discretization_points; ++i) {
for (auto ofs : {-1, 0, 1}) {
if (0 <= i + ofs && i + ofs < discretization_points) {
values[pos] = coefs[ofs + 1];
col_idxs[pos] = i + ofs;
++pos;
}
}
row_ptrs[i + 1] = pos;
}
}
template <typename Closure>
{
const auto discretization_points = rhs->
get_size()[0];
const auto h = 1.0 / (discretization_points + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < discretization_points; ++i) {
const auto xi = (i + 1) * h;
values[i] = -f(xi) * h * h;
}
values[0] += u0;
values[discretization_points - 1] += u1;
}
{
std::cout << u0 << '\n';
for (
int i = 0; i < u->
get_size()[0]; ++i) {
}
std::cout << u1 << std::endl;
}
template <typename Closure>
Closure correct_u)
{
const auto h = 1.0 / (discretization_points + 1);
auto error = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < discretization_points; ++i) {
using std::abs;
const auto xi = (i + 1) * h;
error +=
}
return error;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
using vec = gko::matrix::Dense<double>;
if (argc < 2) {
std::cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " DISCRETIZATION_POINTS [executor]"
<< std::endl;
std::exit(-1);
}
const unsigned int discretization_points =
argc >= 2 ? std::atoi(argv[1]) : 100;
const auto executor_string = argc >= 3 ? argv[2] : "reference";
std::map<std::string, std::shared_ptr<gko::Executor>> exec_map{
{"omp", omp},
{"reference", gko::ReferenceExecutor::create()}};
const auto exec = exec_map.at(executor_string);
const auto app_exec = exec_map["omp"];
auto correct_u = [](double x) { return x * x * x; };
auto f = [](double x) { return 6 * x; };
auto u0 = correct_u(0);
auto u1 = correct_u(1);
auto matrix = mtx::create(app_exec,
gko::dim<2>(discretization_points),
3 * discretization_points - 2);
generate_stencil_matrix(
lend(matrix));
auto rhs = vec::create(app_exec,
gko::dim<2>(discretization_points, 1));
generate_rhs(f, u0, u1,
lend(rhs));
auto u = vec::create(app_exec,
gko::dim<2>(discretization_points, 1));
for (
int i = 0; i < u->
get_size()[0]; ++i) {
}
cg::build()
.with_criteria(gko::stop::Iteration::build()
.with_max_iters(discretization_points)
.on(exec),
.with_reduction_factor(1e-6)
.on(exec))
.with_preconditioner(bj::build().on(exec))
.on(exec)
->generate(
clone(exec, matrix))
print_solution(u0, u1,
lend(u));
std::cout << "The average relative error is "
<< calculate_error(discretization_points,
lend(u), correct_u) /
discretization_points
<< std::endl;
}


![$ u : [0, 1] \rightarrow R\\ u'' = f\\ u(0) = u0\\ u(1) = u1 $](form_15.png)
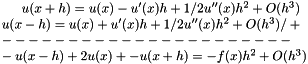
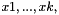 and step size
and step size 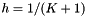 , the formula produces a system of linear equations
, the formula produces a system of linear equations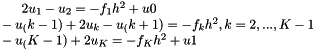
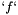 is set to
is set to 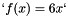 (making the solution
(making the solution 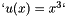 ), but that can be changed in the
), but that can be changed in the  1.8.13
1.8.13