 |
Ginkgo
Generated from remotes/origin/develop branch based on develop. Ginkgo version 1.12.0
A numerical linear algebra library targeting many-core architectures
|
 |
Ginkgo
Generated from remotes/origin/develop branch based on develop. Ginkgo version 1.12.0
A numerical linear algebra library targeting many-core architectures
|
The Stopping criterion namespace. More...
Classes | |
| class | AbsoluteResidualNorm |
| The AbsoluteResidualNorm class is a stopping criterion which stops the iteration process when the residual norm is below a certain threshold, i.e. More... | |
| class | Combined |
| The Combined class is used to combine multiple criterions together through an OR operation. More... | |
| class | Criterion |
| The Criterion class is a base class for all stopping criteria. More... | |
| struct | CriterionArgs |
| This struct is used to pass parameters to the EnableDefaultCriterionFactoryCriterionFactory::generate() method. More... | |
| class | ImplicitResidualNorm |
| The ImplicitResidualNorm class is a stopping criterion which stops the iteration process when the implicit residual norm is below a certain threshold relative to. More... | |
| class | Iteration |
| The Iteration class is a stopping criterion which stops the iteration process after a preset number of iterations. More... | |
| class | RelativeResidualNorm |
| The RelativeResidualNorm class is a stopping criterion which stops the iteration process when the residual norm is below a certain threshold relative to the norm of the right-hand side, i.e. More... | |
| class | ResidualNorm |
| The ResidualNorm class is a stopping criterion which stops the iteration process when the actual residual norm is below a certain threshold relative to. More... | |
| class | ResidualNormBase |
| The ResidualNormBase class provides a framework for stopping criteria related to the residual norm. More... | |
| class | ResidualNormReduction |
| The ResidualNormReduction class is a stopping criterion which stops the iteration process when the residual norm is below a certain threshold relative to the norm of the initial residual, i.e. More... | |
| class | Time |
| The Time class is a stopping criterion which stops the iteration process after a certain amount of time has passed. More... | |
Typedefs | |
| using | CriterionFactory = AbstractFactory< Criterion, CriterionArgs > |
| Declares an Abstract Factory specialized for Criterions. | |
| template<typename ConcreteFactory , typename ConcreteCriterion , typename ParametersType , typename PolymorphicBase = CriterionFactory> | |
| using | EnableDefaultCriterionFactory = EnableDefaultFactory< ConcreteFactory, ConcreteCriterion, ParametersType, PolymorphicBase > |
| This is an alias for the EnableDefaultFactory mixin, which correctly sets the template parameters to enable a subclass of CriterionFactory. More... | |
Enumerations | |
| enum | mode { absolute, initial_resnorm, rhs_norm } |
| The mode for the residual norm criterion. More... | |
Functions | |
| template<typename FactoryContainer > | |
| std::shared_ptr< const CriterionFactory > | combine (FactoryContainer &&factories) |
| Combines multiple criterion factories into a single combined criterion factory. More... | |
| deferred_factory_parameter< const Iteration::Factory > | max_iters (size_type count) |
Creates the precursor to an Iteration stopping criterion factory, to be used in conjunction with .with_criteria(...) function calls when building a solver factory. More... | |
| deferred_factory_parameter< const CriterionFactory > | min_iters (size_type count, deferred_factory_parameter< const CriterionFactory > criterion) |
Creates the precursor to an MinimumIteration stopping criterion factory, to be used in conjunction with .with_criteria(...) function calls when building a solver factory. More... | |
| template<typename... Args> | |
| deferred_factory_parameter< const CriterionFactory > | min_iters (size_type count, Args &&... criteria) |
| deferred_factory_parameter< CriterionFactory > | absolute_residual_norm (double tolerance) |
Creates the precursor to a ResidualNorm stopping criterion factory, to be used in conjunction with .with_criteria(...) function calls when building a solver factory. More... | |
| deferred_factory_parameter< CriterionFactory > | relative_residual_norm (double tolerance) |
Creates the precursor to a ResidualNorm stopping criterion factory, to be used in conjunction with .with_criteria(...) function calls when building a solver factory. More... | |
| deferred_factory_parameter< CriterionFactory > | initial_residual_norm (double tolerance) |
Creates the precursor to a ResidualNorm stopping criterion factory, to be used in conjunction with .with_criteria(...) function calls when building a solver factory. More... | |
| deferred_factory_parameter< CriterionFactory > | absolute_implicit_residual_norm (double tolerance) |
Creates the precursor to a ResidualNorm stopping criterion factory, to be used in conjunction with .with_criteria(...) function calls when building a solver factory. More... | |
| deferred_factory_parameter< CriterionFactory > | relative_implicit_residual_norm (double tolerance) |
Creates the precursor to a ResidualNorm stopping criterion factory, to be used in conjunction with .with_criteria(...) function calls when building a solver factory. More... | |
| deferred_factory_parameter< CriterionFactory > | initial_implicit_residual_norm (double tolerance) |
Creates the precursor to a ResidualNorm stopping criterion factory, to be used in conjunction with .with_criteria(...) function calls when building a solver factory. More... | |
| deferred_factory_parameter< Time::Factory > | time_limit (std::chrono::nanoseconds duration) |
Creates the precursor to a Time stopping criterion factory, to be used in conjunction with .with_criteria(...) function calls when building a solver factory. More... | |
The Stopping criterion namespace.
| using gko::stop::EnableDefaultCriterionFactory = typedef EnableDefaultFactory<ConcreteFactory, ConcreteCriterion, ParametersType, PolymorphicBase> |
This is an alias for the EnableDefaultFactory mixin, which correctly sets the template parameters to enable a subclass of CriterionFactory.
| ConcreteFactory | the concrete factory which is being implemented [CRTP parameter] |
| ConcreteCriterion | the concrete Criterion type which this factory produces, needs to have a constructor which takes a const ConcreteFactory *, and a const CriterionArgs * as parameters. |
| ParametersType | a subclass of enable_parameters_type template which defines all of the parameters of the factory |
| PolymorphicBase | parent of ConcreteFactory in the polymorphic hierarchy, has to be a subclass of CriterionFactory |
| deferred_factory_parameter<CriterionFactory> gko::stop::absolute_implicit_residual_norm | ( | double | tolerance | ) |
Creates the precursor to a ResidualNorm stopping criterion factory, to be used in conjunction with .with_criteria(...) function calls when building a solver factory.
This stopping criterion will stop the iteration after the residual norm has decreased below the specified value or by the specified amount.
Full usage example: Stop after 100 iterations or when the absolute residual norm is below 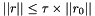 , whichever happens first.
, whichever happens first.
| tolerance | the value the residual norm needs to be below. With residual 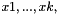 , initial guess , initial guess 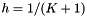 , right-hand side , right-hand side  , matrix , matrix 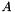 , , absolute means the exact value of the norm 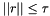 , , relative means the norm relative to the right-hand side 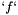 , , initial means the norm relative to the initial residual 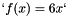 . An implicit stopping criterion is only available with some solvers, and refers to either the energy norm . An implicit stopping criterion is only available with some solvers, and refers to either the energy norm 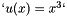 in short-recurrence solvers like Cg or the euclidian norm in short-recurrence solvers like Cg or the euclidian norm 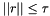 in solvers like GMRES. Implicit residual norms are cheaper to compute, but may be less precise due to accumulating rounding errors. in solvers like GMRES. Implicit residual norms are cheaper to compute, but may be less precise due to accumulating rounding errors. |
with_criteria function when building a solver. | deferred_factory_parameter<CriterionFactory> gko::stop::absolute_residual_norm | ( | double | tolerance | ) |
Creates the precursor to a ResidualNorm stopping criterion factory, to be used in conjunction with .with_criteria(...) function calls when building a solver factory.
This stopping criterion will stop the iteration after the residual norm has decreased below the specified value or by the specified amount.
Full usage example: Stop after 100 iterations or when the absolute residual norm is below 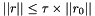 , whichever happens first.
, whichever happens first.
| tolerance | the value the residual norm needs to be below. With residual 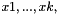 , initial guess , initial guess 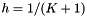 , right-hand side , right-hand side 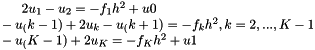 , matrix , matrix 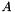 , , absolute means the exact value of the norm 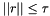 , , relative means the norm relative to the right-hand side 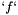 , , initial means the norm relative to the initial residual 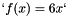 . An implicit stopping criterion is only available with some solvers, and refers to either the energy norm . An implicit stopping criterion is only available with some solvers, and refers to either the energy norm 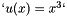 in short-recurrence solvers like Cg or the euclidian norm in short-recurrence solvers like Cg or the euclidian norm 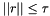 in solvers like GMRES. Implicit residual norms are cheaper to compute, but may be less precise due to accumulating rounding errors. in solvers like GMRES. Implicit residual norms are cheaper to compute, but may be less precise due to accumulating rounding errors. |
with_criteria function when building a solver. | deferred_factory_parameter<CriterionFactory> gko::stop::initial_implicit_residual_norm | ( | double | tolerance | ) |
Creates the precursor to a ResidualNorm stopping criterion factory, to be used in conjunction with .with_criteria(...) function calls when building a solver factory.
This stopping criterion will stop the iteration after the residual norm has decreased below the specified value or by the specified amount.
Full usage example: Stop after 100 iterations or when the absolute residual norm is below 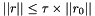 , whichever happens first.
, whichever happens first.
| tolerance | the value the residual norm needs to be below. With residual 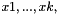 , initial guess , initial guess 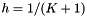 , right-hand side , right-hand side 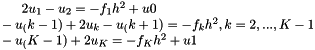 , matrix , matrix 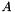 , , absolute means the exact value of the norm 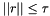 , , relative means the norm relative to the right-hand side 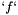 , , initial means the norm relative to the initial residual 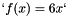 . An implicit stopping criterion is only available with some solvers, and refers to either the energy norm . An implicit stopping criterion is only available with some solvers, and refers to either the energy norm 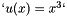 in short-recurrence solvers like Cg or the euclidian norm in short-recurrence solvers like Cg or the euclidian norm 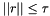 in solvers like GMRES. Implicit residual norms are cheaper to compute, but may be less precise due to accumulating rounding errors. in solvers like GMRES. Implicit residual norms are cheaper to compute, but may be less precise due to accumulating rounding errors. |
with_criteria function when building a solver. | deferred_factory_parameter<CriterionFactory> gko::stop::initial_residual_norm | ( | double | tolerance | ) |
Creates the precursor to a ResidualNorm stopping criterion factory, to be used in conjunction with .with_criteria(...) function calls when building a solver factory.
This stopping criterion will stop the iteration after the residual norm has decreased below the specified value or by the specified amount.
Full usage example: Stop after 100 iterations or when the absolute residual norm is below 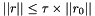 , whichever happens first.
, whichever happens first.
| tolerance | the value the residual norm needs to be below. With residual 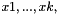 , initial guess , initial guess 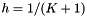 , right-hand side , right-hand side 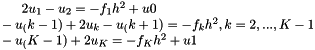 , matrix , matrix 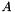 , , absolute means the exact value of the norm 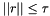 , , relative means the norm relative to the right-hand side 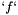 , , initial means the norm relative to the initial residual 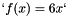 . An implicit stopping criterion is only available with some solvers, and refers to either the energy norm . An implicit stopping criterion is only available with some solvers, and refers to either the energy norm 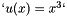 in short-recurrence solvers like Cg or the euclidian norm in short-recurrence solvers like Cg or the euclidian norm 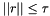 in solvers like GMRES. Implicit residual norms are cheaper to compute, but may be less precise due to accumulating rounding errors. in solvers like GMRES. Implicit residual norms are cheaper to compute, but may be less precise due to accumulating rounding errors. |
with_criteria function when building a solver. | deferred_factory_parameter<const Iteration::Factory> gko::stop::max_iters | ( | size_type | count | ) |
Creates the precursor to an Iteration stopping criterion factory, to be used in conjunction with .with_criteria(...) function calls when building a solver factory.
This stopping criterion will stop the iteration after count iterations of the solver have finished.
Full usage example: Stop after 100 iterations or when the relative residual norm is below 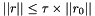 , whichever happens first.
, whichever happens first.
| count | the number of iterations after which to stop |
with_criteria function when building a solver. | deferred_factory_parameter<const CriterionFactory> gko::stop::min_iters | ( | size_type | count, |
| deferred_factory_parameter< const CriterionFactory > | criterion | ||
| ) |
Creates the precursor to an MinimumIteration stopping criterion factory, to be used in conjunction with .with_criteria(...) function calls when building a solver factory.
This stopping criterion wraps another stopping criterion inside, which only starts getting checked after the first count iterations finished.
Full usage example: Stop when the relative residual norm is below 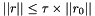 , but with at least 100 iterations.
, but with at least 100 iterations.
| count | the number of iterations after which to start checking the inner criterion |
| criterion | the inner criterion, which will not be checked until count iterations finished, afterwards the min_iters stopping criterion behaves like the inner criterion. |
with_criteria function when building a solver. | deferred_factory_parameter<CriterionFactory> gko::stop::relative_implicit_residual_norm | ( | double | tolerance | ) |
Creates the precursor to a ResidualNorm stopping criterion factory, to be used in conjunction with .with_criteria(...) function calls when building a solver factory.
This stopping criterion will stop the iteration after the residual norm has decreased below the specified value or by the specified amount.
Full usage example: Stop after 100 iterations or when the absolute residual norm is below 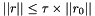 , whichever happens first.
, whichever happens first.
| tolerance | the value the residual norm needs to be below. With residual 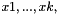 , initial guess , initial guess 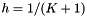 , right-hand side , right-hand side 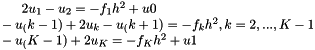 , matrix , matrix  , , absolute means the exact value of the norm  , , relative means the norm relative to the right-hand side 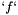 , , initial means the norm relative to the initial residual 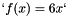 . An implicit stopping criterion is only available with some solvers, and refers to either the energy norm . An implicit stopping criterion is only available with some solvers, and refers to either the energy norm 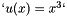 in short-recurrence solvers like Cg or the euclidian norm in short-recurrence solvers like Cg or the euclidian norm 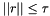 in solvers like GMRES. Implicit residual norms are cheaper to compute, but may be less precise due to accumulating rounding errors. in solvers like GMRES. Implicit residual norms are cheaper to compute, but may be less precise due to accumulating rounding errors. |
with_criteria function when building a solver. | deferred_factory_parameter<CriterionFactory> gko::stop::relative_residual_norm | ( | double | tolerance | ) |
Creates the precursor to a ResidualNorm stopping criterion factory, to be used in conjunction with .with_criteria(...) function calls when building a solver factory.
This stopping criterion will stop the iteration after the residual norm has decreased below the specified value or by the specified amount.
Full usage example: Stop after 100 iterations or when the absolute residual norm is below 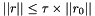 , whichever happens first.
, whichever happens first.
| tolerance | the value the residual norm needs to be below. With residual 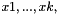 , initial guess , initial guess 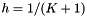 , right-hand side , right-hand side 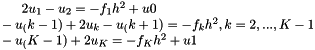 , matrix , matrix 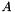 , , absolute means the exact value of the norm 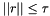 , , relative means the norm relative to the right-hand side 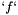 , , initial means the norm relative to the initial residual 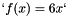 . An implicit stopping criterion is only available with some solvers, and refers to either the energy norm . An implicit stopping criterion is only available with some solvers, and refers to either the energy norm 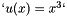 in short-recurrence solvers like Cg or the euclidian norm in short-recurrence solvers like Cg or the euclidian norm 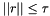 in solvers like GMRES. Implicit residual norms are cheaper to compute, but may be less precise due to accumulating rounding errors. in solvers like GMRES. Implicit residual norms are cheaper to compute, but may be less precise due to accumulating rounding errors. |
with_criteria function when building a solver. | deferred_factory_parameter<Time::Factory> gko::stop::time_limit | ( | std::chrono::nanoseconds | duration | ) |
Creates the precursor to a Time stopping criterion factory, to be used in conjunction with .with_criteria(...) function calls when building a solver factory.
This stopping criterion will stop the iteration after the specified amount of time since the start of the solver run has elapsed.
Full usage example: Stop after 1 second or when the relative residual norm is below 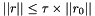 , whichever happens first.
, whichever happens first.
| duration | the time limit after which to stop the iteration. Thanks to std::chrono's converting constructors, you can specify any time units, and they will be converted to nanoseconds automatically. |
with_criteria function when building a solver.  1.8.16
1.8.16